Common Neurologists Diagnoses & Treated Conditions
- infections of the nervous system, including encephalitis, meningitis, or brain abscesses
- neurodegenerative disorders, such as Lou Gehrig’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease
- spinal cord disorders, including inflammatory and autoimmune disorders
- seizure disorders, such as epilepsy
- stroke
- multiple sclerosis
- neuromuscular disorders, such as myasthenia gravis
- headaches, such as cluster headaches and migraines
"Lawrence in the EEG department was phenomenal. Such a kind young man, he was able to answer all my questions and put me at ease before doing the test. He is very knowledgeable and enthusiastic about what he does."
- Anonymous Patient
How a Diagnosis is Made
To make a diagnosis, a neurologist may use imaging tests such as:
- computed tomography, or CT scan
- magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI scan
- positron emission tomography, or PET scan
A neurologist may also require psychical tests in order to make a formal diagnosis, such as:
Neurological Exam
Typically, the exam tests vision, strength, coordination, reflexes, and sensation.
Lumbar puncture
Your neurologist may use a lumbar puncture to test your spinal fluid. They may recommend the procedure if they believe your symptoms are caused by a problem in your nervous system that can be detected in your spinal fluid.
The procedure involves inserting a needle into the spine after numbing it and taking a sample of spinal fluid.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
This test measures electrical activity in the brain, by applying small electrodes to your head.
Other diagnostic procedures include sleep studies and angiography. Angiography determines blockages in the blood vessels going to the brain.
Your neurologist may help you manage your symptoms and neurological disorder alone, or work with your primary care physician and other specialists.
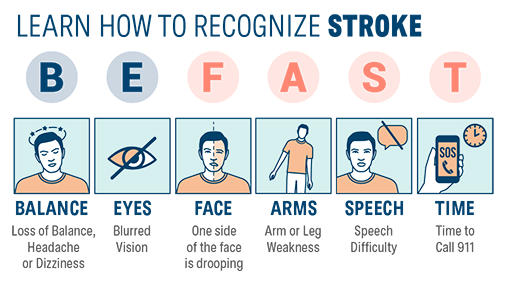
Use the B.E. F.A.S.T. Test
Learn how to recognize a Stroke
- Balance: Loss of balance, headache, dizziness
- Eyes: The person may be experiencing blurred vision.
- Face: Ask the person to smile. Is the face lopsided?
- Arm: Ask the person to raise their arms. Does one arm drift down?
- Speech: Ask the person to repeat a phrase. Does their speech sound strange? Can they do it without slurring words?
- Time: Don't waste it. Call 911 now.